Need an audio CD ripper? Try Audio Transcoder!
Convert and encode (rip) audio CDs (.cda files) on Windows with an audio CD ripper called 'Audio Transcoder'!
Audio Transcoder is an audio CD ripper, cd to mp3 converter, audiograbber which allows you to rip cd to flac, rip cd to mp3, rip cda to mp3, rip cd to aac, rip cd to aiff, rip cd to ape, rip cd to flac, rip cd to alac, rip cd to m4a, rip cd to mpc, rip cd to ogg, rip cd to wav, rip cd to wma etc. Advanced options are available for those who want to take advantage of them, though they are completely optional, making Audio Transcoder the perfect MP3 ripper software for users of any experience level. The audio format conversions are performed without any temporary files, allowing high conversion speeds. Other features include support for ID3, OGG, WMA, FLAC tags and more.
Audio CD Ripper main features:
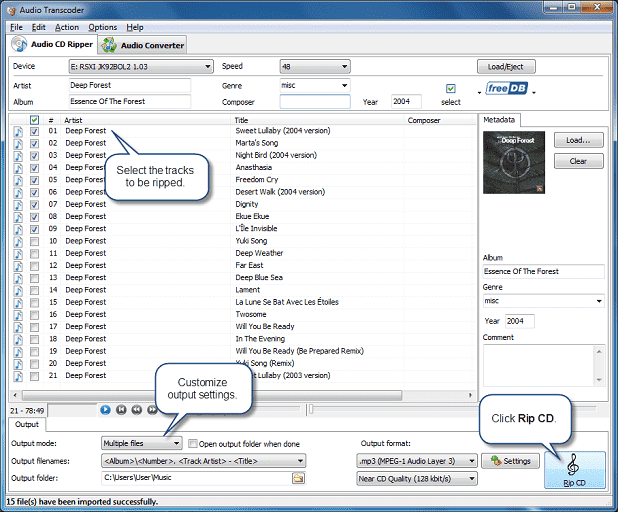 |
• Rip (convert) audio tracks from audio CD's to AAC, M4A (iPod AAC and Apple Lossless(ALAC)), M4B, MP4, MP3, MusePack(MPC), Ogg, WMA, FLAC, APE, WAV, Speex(SPX), MP2 and WAV formats with different settings.
• Fast Conversion Speed: Audio format conversion is performed directly without any temporary files, thus enabling high converting speed and economy of hard disk resources.
• Supports automatic saving ID3 tags when converting, and also supports ID3 tags display and edit.
• Easy-to-use user-friendly interface.
• Rip audio CDs to audio image (audio+cue files)
• Rip and convert CDs
• Rip & encode CD music
• Rip audio CD to MP3
• Convert CD to MP4
• Rip CD music to WMA
• Convert CDA to WAV
• Rip CDA to AAC files
• Convert CDA to OGG
• Encode CDA to FLAC
• Convert CDA to APE
• Get disc information from Internet disc database (FreeDB)
• Full media tags support for each audio format: AAC (AAC, M4A, M4B, MP4), MP3, MP2,MusePack(MPC), Ogg, WMA, FLAC, APE, WAV, Speex(SPX).
• Play audio in the built-in CD-player
• Read CD-text
• Ability to play tracks prior to conversion.
Supported File Formats:
Input Formats: CDA
Output Formats: AAC, M4A (iPod AAC and Apple Lossless(ALAC)), M4B, MP4, MP3, MusePack(MPC), Ogg, WMA, FLAC, APE, WAV, Speex(SPX), MP2 and WAV formats.
Audio CD Ripper System Requirements:
-
Minimum System Requirements
- Microsoft Windows XP/Windows Vista/Windows 7/Windows 8/8.1(32-bit and 64-bit)
- 1.0 GHz or faster processor
- 512 MB RAM
- 10 MB free hard drive space
-
Recommended System Requirements
- Microsoft Windows XP/Windows Vista/Windows 7/Windows 8/8.1 (32-bit and 64-bit)
- Pentium 4 or faster multi-core processor
- 1 GB RAM
- 10 MB free hard drive space
Frequently Asked Questions:
How to uninstall Audio CD Ripper?
How do I uninstall Audio CD Ripper in Windows Vista / Windows 7 / Windows 8 / Windows 8.1 / Windows 10?
Click “Start”
Click on “Control Panel”
Under Programs click the Uninstall a Program link.
Select “Audio CD Ripper” and right click, then select Uninstall/Change.
Click “Yes” to confirm the uninstallation.
How do I uninstall Audio CD Ripper in Windows XP?
Click “Start”
Click on “Control Panel”
Click the Add or Remove Programs icon.
Click on “Audio CD Ripper”, then click “Remove/Uninstall.”
Click “Yes” to confirm the uninstallation.
How do I uninstall Audio CD Ripper in Windows 2000?
Click “Start”
Click on “Control Panel”
Double-click the “Add/Remove Programs” icon.
Select “Audio CD Ripper” and right click, then select Uninstall/Change.
Click “Yes” to confirm the uninstallation.
How do I access the Audio CD Ripper download for PC?
It’s easy! Just click the Audio CD Ripper download button at the page. Clicking this link will start the installer to download Audio CD Ripper free for Windows.
Will this Audio CD Ripper download work on Windows?
Yes! The Audio CD Ripper download for PC works on most current Windows operating systems.
What is CD Audio?
Compact Disc Digital Audio (CDDA or CD-DA) is the standard format for audio compact discs. The standard is defined in the Red Book, one of a series of "Rainbow Books" (named for their binding colors) that contain the technical specifications for all CD formats. The audio contained in a CD-DA consists of two-channel signed 16-bit Linear PCM sampled at 44,100 Hz. Each audio sample is a signed 16-bit two's complement integer, with sample values ranging from ?32768 to +32767. The source audio data is divided into frames, containing twelve samples each (six left and right samples, alternating), for a total of 192 bits (24 bytes) of audio data per frame. This stream of audio frames, as a whole, is then subjected to CIRC encoding, which segments and rearranges the data and expands it with parity bits in a way that allows occasional read errors to be detected and corrected. CIRC encoding also interleaves the audio frames throughout the disc over several consecutive frames so that the information will be more resistant to burst errors. Therefore, a physical frame on the disc will actually contain information from multiple logical audio frames. This process adds 64 bits of error correction data to each frame. After this, 8 bits of subcode or subchannel data are added to each of these encoded frames, which is used for control and addressing when playing the CD. CIRC encoding plus the subcode byte generate 33-bytes long frames, called "channel-data" frames. These frames are then modulated through eight-to-fourteen modulation (EFM), where each 8-bit word is replaced with a corresponding 14-bit word designed to reduce the number of transitions between 0 and 1. This reduces the density of physical pits on the disc and provides an additional degree of error tolerance. Three "merging" bits are added before each 14-bit word for disambiguation and synchronization. In total there are 33 ? (14 + 3) = 561 bits. A 27-bit word (a 24-bit pattern plus 3 merging bits) is added to the beginning of each frame to assist with synchronization, so the reading device can locate frames easily. With this, a frame ends up containing 588 bits of "channel data" (which are decoded to only 192 bits music). The frames of channel data are finally written to disc physically in the form of pits and lands, with each pit or land representing a series of zeroes, and with the transition points—the edge of each pit—representing 1. A Red Book-compatible CD-R has pit-and-land-shaped spots on a layer of organic dye instead of actual pits and lands; a laser creates the spots by altering the reflective properties of the dye.